1.3 Main topics, key concepts, and terminologies#
1.3.1 Main topics discussed#
The Handbook chapters cover the following main topics:
Institutional and organizational frameworks securing resilience and the adaptability of official statistics;
Communication, advocacy, and multi-stakeholder partnerships for official statistics;
Production processes and data sources for integrated production systems in official statistics;
Information technology infrastructure to support data collection and the sharing, processing, and dissemination of official statistics;
Quality assurance frameworks, quality policy and quality management in official statistics;
Capacity development, training, and resource mobilisation in official statistics.
The presentations and discussions are based on the most recent versions of the Global Inventory of Statistical Standards[footnote1], concepts and definitions, classifications, and methodologies when writing the Handbook. The standards are presented and discussed in the specific chapters that refer to them.
Where necessary, the evolution and changes in the standards are presented. In discussing standards-based modernisation of the statistical production process, the Generic Statistical Business Process Model (GSBPM) is used as the organising framework. The discussion on the management of statistical activities is loosely based on another modernisation standard linked to the GSBPM—the Generic Activity Model for Statistical Organizations (GAMSO). A schematic diagram of the GAMSO and its relationship to GSBPM is displayed in Figure 3.
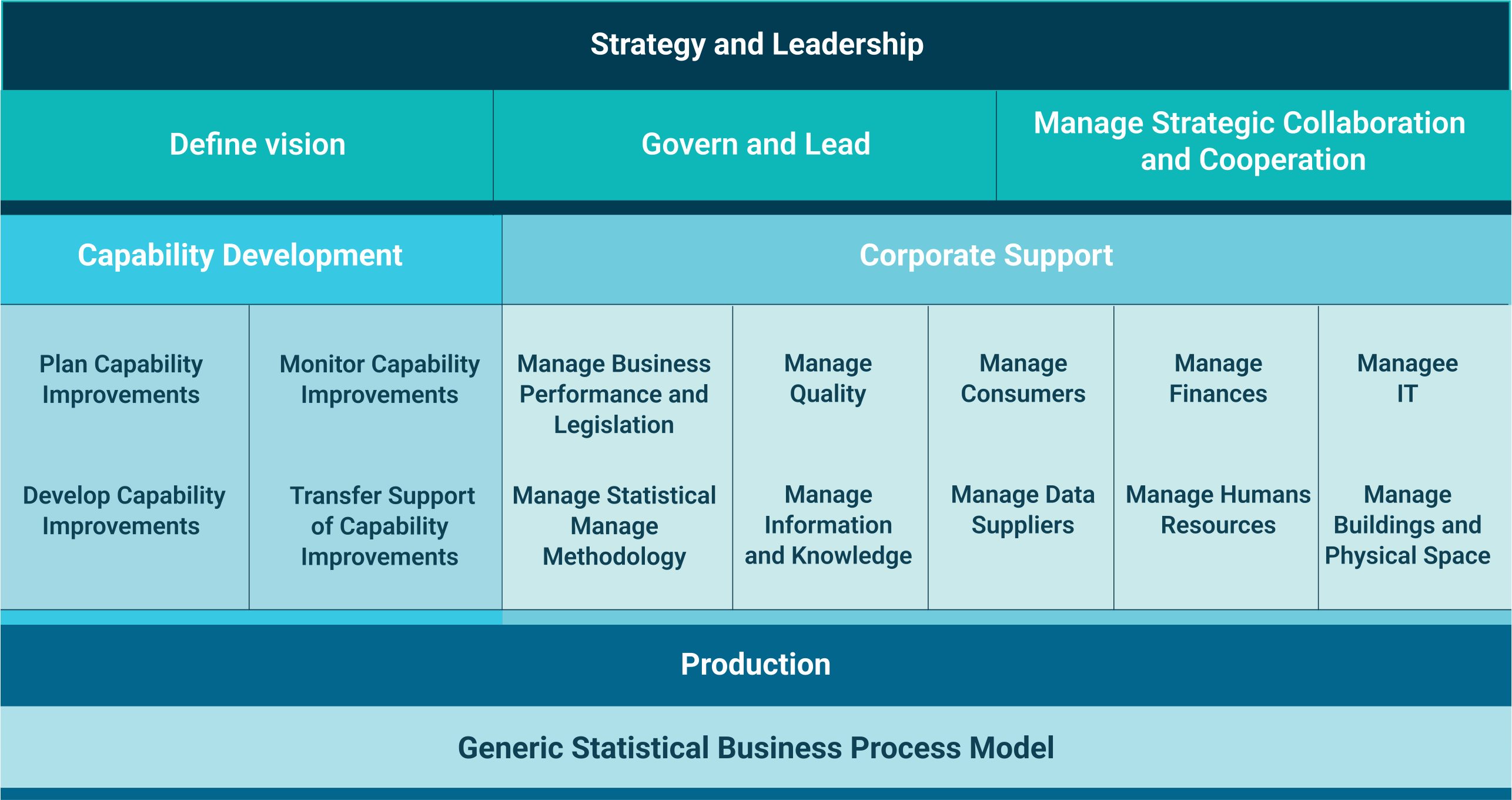
Fig. 3 Activity areas of GAMSO
Source: Adapted from: https://statswiki.unece.org/display/GAMSO/II.+Structure#
1.3.2 Key concepts and definitions#
Each chapter introduces the terminologies and defines the key concepts necessary to have a common basis for understanding the topics. In addition, the Handbook has a Glossary that serves as a compilation of key terms and their definitions, along with explanatory notes where needed. A list and description of statistical applications, software and modernisation models and standards is also included in the Handbook.
The key concepts and terminologies in this handbook on the management of national statistical systems are the national statistical office, other producers of official statistics, official statistics, and the national statistical system defined as follows in the Glossary and further developed in - The Basis of Official Statistics:
The national statistical office (NSO) is defined as the main producer of official statistics in a country and/or the organization responsible for coordinating all activities related to the development, production, and dissemination of official statistics in the national statistical system.
An other producer of Official Statistics (OPOS) is an organizational entity within a government ministry, department, or agency, other than the national statistical office, that develops, produces and disseminates official statistics.
Official statistics are defined as statistics produced according to the Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics (UNFPOS) by a national statistical office or by another producer of official statistics mandated by the national government or certified by the national statistical office to compile statistics for its specific domain.
The national statistical system (NSS), or national system of official statistics, comprises the national statistical office (NSO) and all other producers of official statistics in the country.
The data ecosystem defined as the entire network of data collectors, data producers, data analysts and other data users that directly or indirectly collect, process disseminate, analyse and/or otherwise consume data and associated services within a specified country or region.
Typically, official statistics are produced and disseminated in compliance with the respective national statistical legislation and identified as such in the national statistical programmes.
All statistics produced by a national statistical office (NSO) are assumed to be official statistics except for those explicitly stated by the NSO as not official. Statistics produced by NSOs that might not be considered official statistics would be methodological studies that have not been adopted officially such as studies on seasonal adjustment procedures or experimental statistics using new methods or data sources.
Most countries have one organization for which the development, production and dissemination of official statistics is the core function. The name of this organization differs among countries (e.g. National Statistical Institute (NSI), National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), National Statistical Agency (NSA), Central Statistical Agency (CSA), Central Statistics/Statistical Office (CSO), etc.). Another practice in naming the organization follows the form “Statistics [name of country]”. In this handbook, the term used is the national statistical office (NSO), defined above. In general, the NSO is the biggest producer of official statistics. It is typically responsible for major data collection activities for official statistics and, in most cases, the population census.
Countries have found different ways of placing the NSO within their administrative structure and in a few cases as an autonomous agency outside the main branch of the executive. In most cases, the function of chief statistician is assigned to the head of the NSO. Chapter 5 - The National Statistical Office discusses various aspects of the NSO as an organization. It includes its vision, mission statement, core function, strategic planning, finance and administrative structures. Chapter 5 also discusses statistical business architecture (🔗) project management and various options for (re) organising the NSO.
Chapter 4 - The National Statistical System further examines organizational issues for national statistical systems derived from the principles and the definition of official statistics and how these principles are translated into institutional safeguards for the various actors in official statistics. The chapter also discusses relationships between the NSO and other producers of official statistics; the ways NSSs are organised (the spectrum from centralised to decentralised, vertically and horizontally, etc.); legislative frameworks and governance; and the chief statistician position and function.
The data ecosystem within a country is broader than the national statistical system because it includes not only those producing official statistics but all producers and users of data in a country.
Considering and understanding the various issues, models, and practices in relation to one’s own NSS and functioning of the NSO and other producers of official statistics are significantly useful in undertaking transformative change, adopting modernisation principles and tools, and managing the resulting changes.
Annex 3 - Evolution of Usage of Terms in the Handbook Series provides an overview of how these definitions have progressed across the time dimensions represented by the three versions of the Handbook.
[footnote1]: The Global Inventory of Statistical Standards is a work in progress and an updated version with improved content and functionalities should be available soon.





