3.1 Introduction#
The key concept and the main topic in this handbook are official statistics. This chapter seeks to clarify what is meant by official statistics, the principles that should guide the production of official statistics, and how these principles can be implemented through legislation and guidelines.
3.1.1 Defining official statistics#
The concept of official statistics in this handbook is based on the UN Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics (UNFPOS). They promote that official statistics should adhere to well-defined professional and scientific standards, while clearly defining the content and identifying the producers of the statistics. A number of principles, codes and legislative initiatives have contributed to clarifying the concepts outlined in the UNFPOS. Thus, in the context of this Handbook Official statistics[1] are defined as comprising the following three elements:

Statistics describing the economic, demographic, social and environmental phenomena meeting diverse user requirements, at different geographical levels from sub-national, via national to supranational and international level.
Statistics developed, produced and disseminated in compliance with the United Nations Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics as well as internationally agreed statistical standards, codes and recommendations fostering trust and ensuring consistent and high quality.
Statistics normally produced by a national statistical office (NSO) and other entities designated as producers of official statistics and indicated as official statistics in relevant legislation and in statistical programmes and documents.
The concept of official statistics used in this Handbook is further defined in Chapter 3.2 — UN Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics, Chapter 3.4 — Legislative frameworks and Chapter 3.5 — Certification and branding of official statistics. In addition, it will also be covered in Chapter 4 - The National Statistical System and Chapter 7 - Quality Management. It is essential to underline that proper quality criteria are closely linked to the concept of official statistics as used in this handbook.
3.1.2 The importance of official statistics#
Official statistics should be a cornerstone of a modern society by providing an unbiased and accurate picture of the economic, demographic, social and environmental situation and development in a country.
To an increasing degree, high quality and comparable statistics are also important for analysis and decision-making at the international and global level. Thus, it is essential that official statistics can be trusted by all users and stakeholders and are made accessible and understandable for all users.
A great deal of statistics is also being produced by private and public agencies that are not part of the system of official statistics. Statistics of questionable quality and proper documentation can be potentially confusing and lead to distrust of the national statistical office (NSO) which is supposed to produce unbiased and high-quality official statistics. Therefore, it is of utmost importance that those statistics considered to be ‘official’ follow strict and well-defined principles and standards.
A more in-depth discussion of official statistics and its importance is provided in Recommendations for promoting, measuring and communicating the value of official statistics, UNECE 2018 (🔗).
3.1.3 The need for the UN Fundamental Principles#
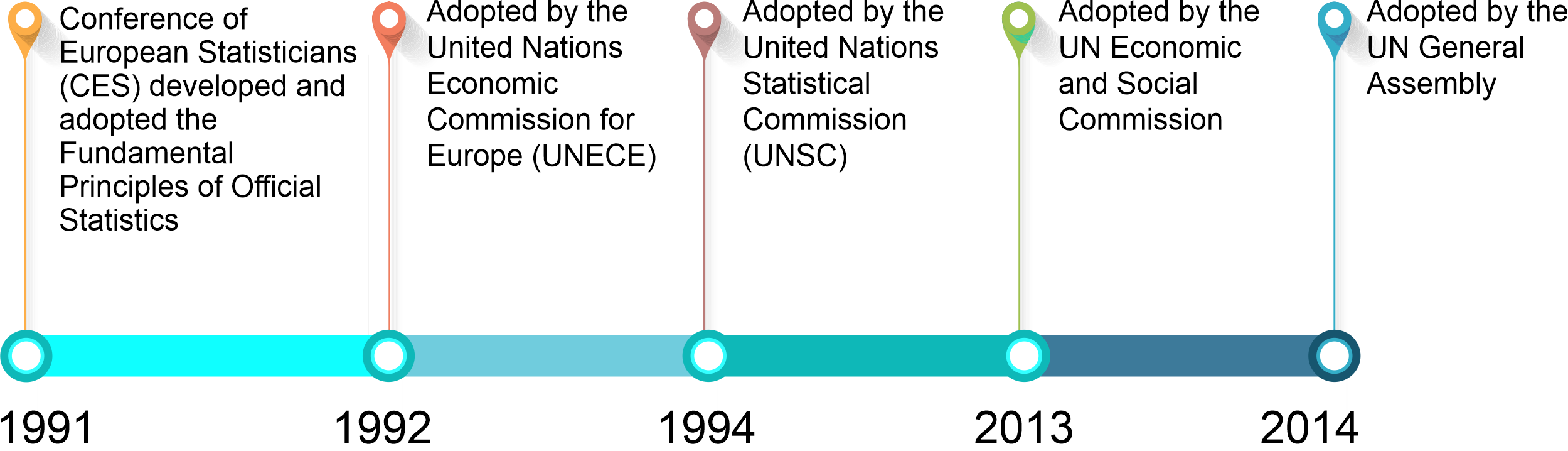
The need for a set of principles governing official statistics became apparent at the end of the 1980s when countries in Central Europe began to change from centrally planned economies to market-oriented democracies. To re-establish trust in these and similar countries’ official statistics, it was essential to ensure that their national statistical systems (NSSs) would produce appropriate and reliable statistics that adhered to established professional and scientific standards. To this end, the Conference of European Statisticians (CES) developed and adopted the Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics in 1991, which were subsequently adopted in 1992 at the ministerial level by Economic Commission of Europe. Statisticians in other parts of the world soon realized that the principles were not necessarily a European phenomenon but were of much wider, global significance. Following an international consultation process, a milestone in the history of international statistics was reached when the United Nations Statistical Commission at its Special Session of 11-15 April 1994 adopted the same set of principles – with a revised preamble – as the United Nations Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics (UNFPOS) .
To be effective, the UNFPOS need to be respected by all stakeholders and at all political levels. Thus, the principles were reaffirmed by the Statistical Commission in 2013 and endorsed by the Economic and Social Council in its resolution 2013/21 of 24 July 2013. Finally, the UN Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics (🔗) were adopted on 29 January 2014 at the highest political level as a General Assembly resolution (A/RES/68/261).
These principles and the related Implementation Guidelines (🔗) are covered in Chapter 3.2 — UN Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics There are several other international principles and guidelines that partly cover the same topics as the UNFPOS. These are described in detail in Chapter 3.3 — Other principles practices and guidelines.
3.1.4 Implementing the UN Fundamental Principles#
International statistical principles and good practices must be implemented and followed within each national statistical system (NSS) using national legal frameworks and guidelines. The Implementation Guidelines provide advice regarding implementation of legal frameworks, which is further elaborated in Chapter 3.4 — Legislative frameworks based on the reference document Guidance on modernising statistical legislation (UNECE 2018) (🔗). This document describes in more detail the implementation of legislation in the field of statistics and builds on and provides some extensions and modification to The Generic Law on Official Statistics (GLOS), adopted by the UNECE 2016. An equivalent generic law was adopted for Latin America by the Statistical Conference of the Americas, Generic Law on Official Statistics for Latin America (GLOS-LA). These documents represent the efforts to develop a model legal framework for legislation in the field of official statistics based on the UNFPOS and taking into consideration other well-established principles.
When discussing official statistics, it is necessary to differentiate between national and international activities in the field of official statistics. Thus, some parts of this chapter, and of this Handbook, might be more relevant to NSOs than to international agencies. There are also some specific challenges for international agencies that are not covered in detail in this handbook and further articulated in Principles Governing International Statistical Activities (🔗). An additional reference is the UN Statistics Quality Assurance Framework (🔗) that targets UN agencies as well as international and national users of statistics.
The practical implementation of fundamental principles and legislative procedures is further developed in Chapter 4 - The National Statistical System, Chapter 5 - The National Statistical Office, Chapter 7 - Quality Management and Chapter 10 - Dissemination of Official Statistics.
