2.3 Basis of official statistics#
Official statistics were originally thus named because they were produced by national statistical offices (NSOs) and other specialised institutions on behalf of national authorities – governments – in the different countries of the world.
The term official statistics has come to refer not only to the producers of the statistics but also to the fact that their activities and outputs are expected to conform to a set of international standards and norms as regards their relevance for the phenomena they are supposed to describe, their quality, impartiality, transparency and coverage.
Following the remarkable convergence of official statistics in countries across the world, culminating in the generally accepted UNFPOS, a modern definition of official statistics reflects this common ground and the principles governing the conditions for and production of the statistics. Hence, official statistics are currently defined as statistics developed, produced and disseminated by the national statistical systems of countries in conformity with the United Nations Fundamental Principles of Official Statistics, internationally agreed statistical standards, codes and recommendations as well as applicable national legislation and programmes.
As mentioned above, the UNFPOS provide the ground rules for the conduct of official statistics. The UNFPOS are composed of a preamble on the fundamental importance of official statistics and ten principles on the conduct of these.
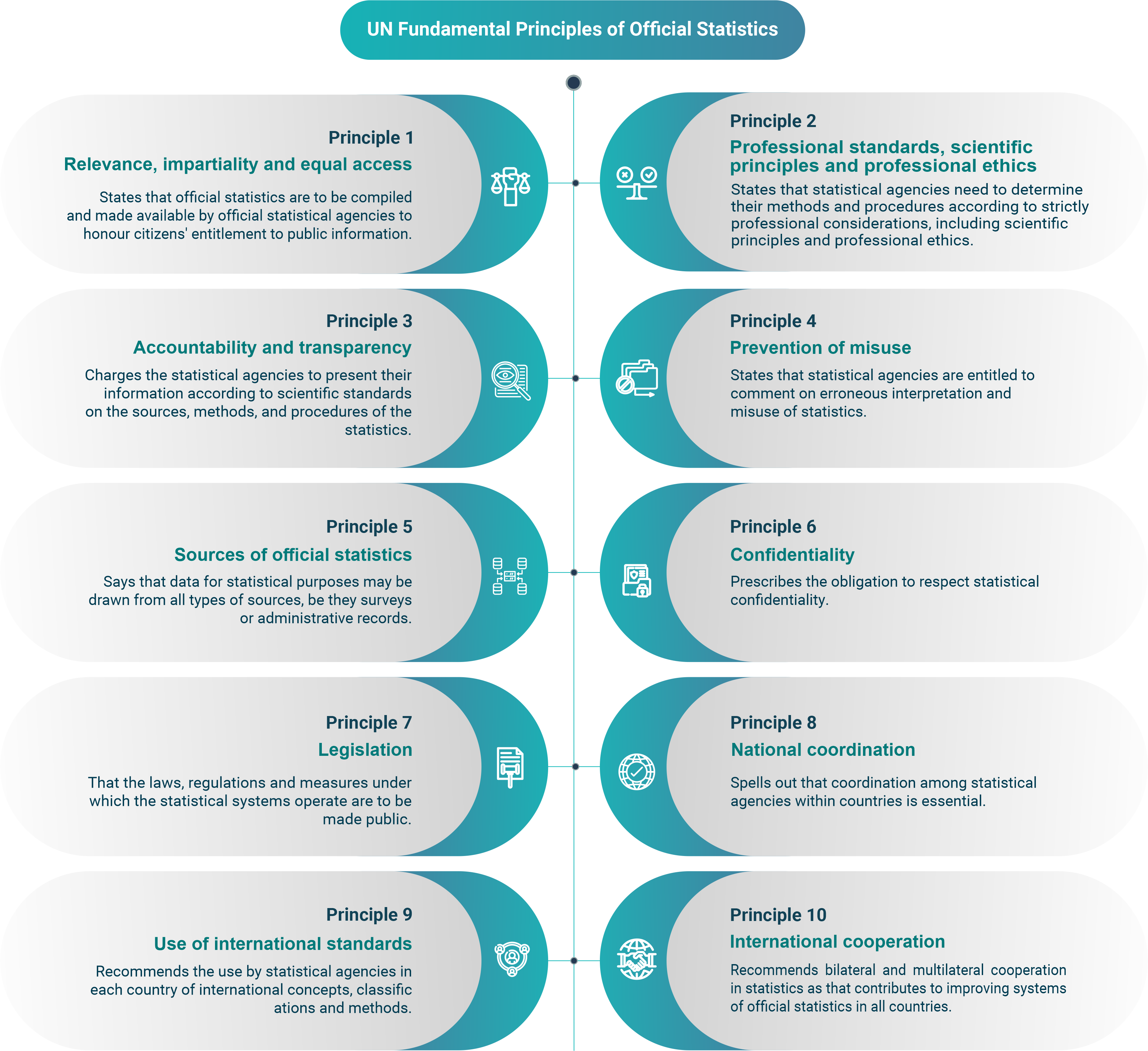
Principle 1 states that official statistics are to be compiled and made available by official statistical agencies to honour citizens’ entitlement to public information. Principle 2 states that statistical agencies need to determine their methods and procedures according to strictly professional considerations, including scientific principles and professional ethics. Principle 3 charges the statistical agencies to present their information according to scientific standards on the sources, methods, and procedures of the statistics. Principle 4 states that statistical agencies are entitled to comment on erroneous interpretation and misuse of statistics. Principle 5 says that data for statistical purposes may be drawn from all types of sources, be they surveys or administrative records. Principle 6 prescribes the obligation to respect statistical confidentiality and principle 7 that the laws, regulations and measures under which the statistical systems operate are to be made public. Principle 8 spells out that coordination among statistical agencies within countries is essential and principle 9 recommends the use by statistical agencies in each country of international concepts, classifications and methods. Finally, principle 10 recommends bilateral and multilateral cooperation in statistics as that contributes to improving systems of official statistics in all countries.